
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
Inorganic halide perovskites (IHPs) have received substantial attention due to their unique optoelectronic properties. Among all the intriguing performance, the efficient luminescence of IHPs enables the practical application of white light-emitting diodes (WLEDs) for lighting. During the last decade, IHP-based white lighting sources with a high luminesce and a broad color gamut have been developed as strong competitors to conventional and classic WLEDs based on rare-earth phosphors and blue LED chips. Thus, it inspires us to give an overview of the emerging progress of IHP WLEDs that can function as lighting sources. Here, in this review, the generation of luminescent properties and white light in IHPs are first presented. Then, both photoluminescence and electroluminescence WLEDs with IHPs emitters, including both lead-based and lead-free IHPs, are synthetically discussed to exhibit their advantages. Furthermore, the efforts on the optical performance enhancement of IHPs in WLEDs are demonstrated and summarized. Apart from WLEDs, visible light communication based on IHPs featuring efficient luminescence is proposed to highlight their promising potential in lighting communication. Finally, some perspectives on the evolution and challenges are described, followed by an inspirational outlook on their future development.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(4): 04001039

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & System (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
Solution-processed oxide semiconductors have been considered as a potential alternative to vacuum-based ones in printable electronics. However, despite spin-coated InZnO (IZO) thin-film transistors (TFTs) have shown a relatively high mobility, the lack of carrier suppressor and the high sensitivity to oxygen and water molecules in ambient air make them potentially suffer issues of poor stability. In this work, Al is used as the third cation doping element to study the effects on the electrical, optoelectronic, and physical properties of IZO TFTs. A hydrophobic self-assembled monolayer called octadecyltrimethoxysilane is introduced as the surface passivation layer, aiming to reduce the effects from air and understand the importance of top surface conditions in solution-processed, ultra-thin oxide TFTs. Owing to the reduced trap states within the film and at the top surface enabled by the doping and passivation, the optimized TFTs show an increased current on/off ratio, a reduced drain current hysteresis, and a significantly enhanced bias stress stability, compared with the untreated ones. By combining with high-capacitance AlOx, TFTs with a low operating voltage of 1.5 V, a current on/off ratio of > 10 4 and a mobility of 4.6 cm2/(V·s) are demonstrated, suggesting the promising features for future low-cost, low-power electronics.
Journal of Semiconductors
2022, 43(3): 034102

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
Inorganic cesium lead halide (, , Br, I) nanocrystals (NCs) attract extensive attention because of their excellent optoelectronic performance. However, the classic NCs suffer from toxicity and instability, which impede their further applications in commercial fields. Here the inorganic lead-free cesium copper chlorine NCs are synthesized by a facile hot-injection method. The blue-emission 3D and green-emission 0D NCs are prepared at 70°C and 120°C, respectively, suggesting that the reaction temperature may account for the final components. Owing to the self-trapped exciton effect, the unique optical properties, such as high photoluminescence (PL) quantum yield, broadband emission, large Stokes shift, and long PL decay time, are demonstrated for both cesium copper chlorine NCs. Moreover, highly efficient and stable warm white light-emitting diodes are fabricated with and NCs. The study highlights the promising potential for lead-free cesium copper chlorine nanocrystals in nontoxic solid-state lighting applications.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(2): 02000187
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
4 e-mail: dujuan@mail.siom.ac.cn
5 e-mail: zangzg@cqu.edu.cn
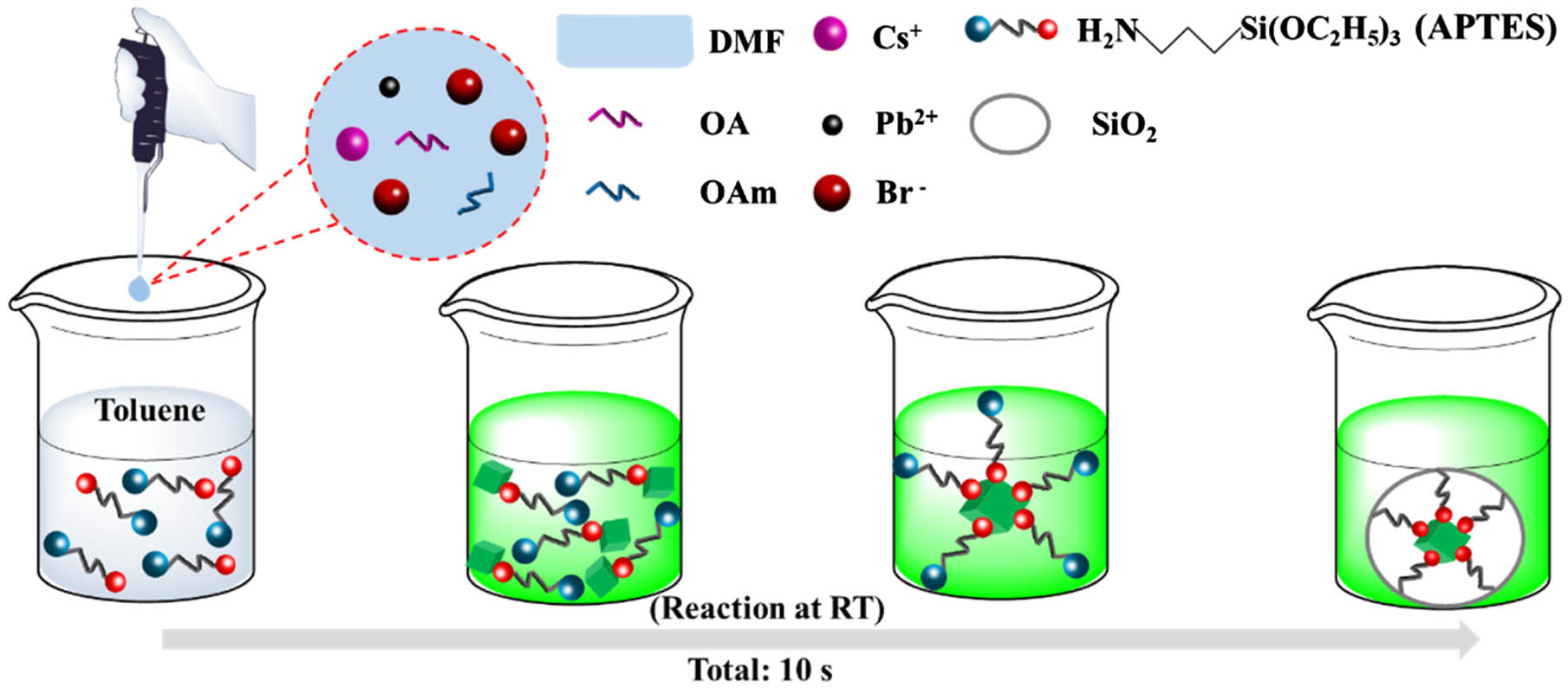
All-inorganic cesium lead bromide () perovskite quantum dots (QDs) with excellent optical properties have been regarded as good gain materials for amplified spontaneous emission (ASE). However, the poor stability as the results of the high sensitivity to heat and moisture limits their further applications. Here, we report a facile one-pot approach to synthesize QDs at room temperature. Due to the effective defects passivation using , as-prepared QDs present an enhanced photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) and chemical stability. The PLQY of QDs reaches 71.6% which is higher than 46% in pure QDs. The PL intensity of QDs maintains 84% while remaining 24% in pure after 80 min heating at 60°C. The ASE performance of the films is also studied under a two-photon-pumped laser. Compared with the films using pure QDs, those with as-prepared QDs exhibit a reduced threshold of ASE. The work suggests that room-temperature-synthesized -coated perovskites QDs are promising candidates for laser devices.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(10): 10001605





